Smart Building solutions are complex, with many integral technologies. It takes multiple intelligent components to bring buildings in line with their Net Zero mission. Here are some behind-the-scenes details about these components.
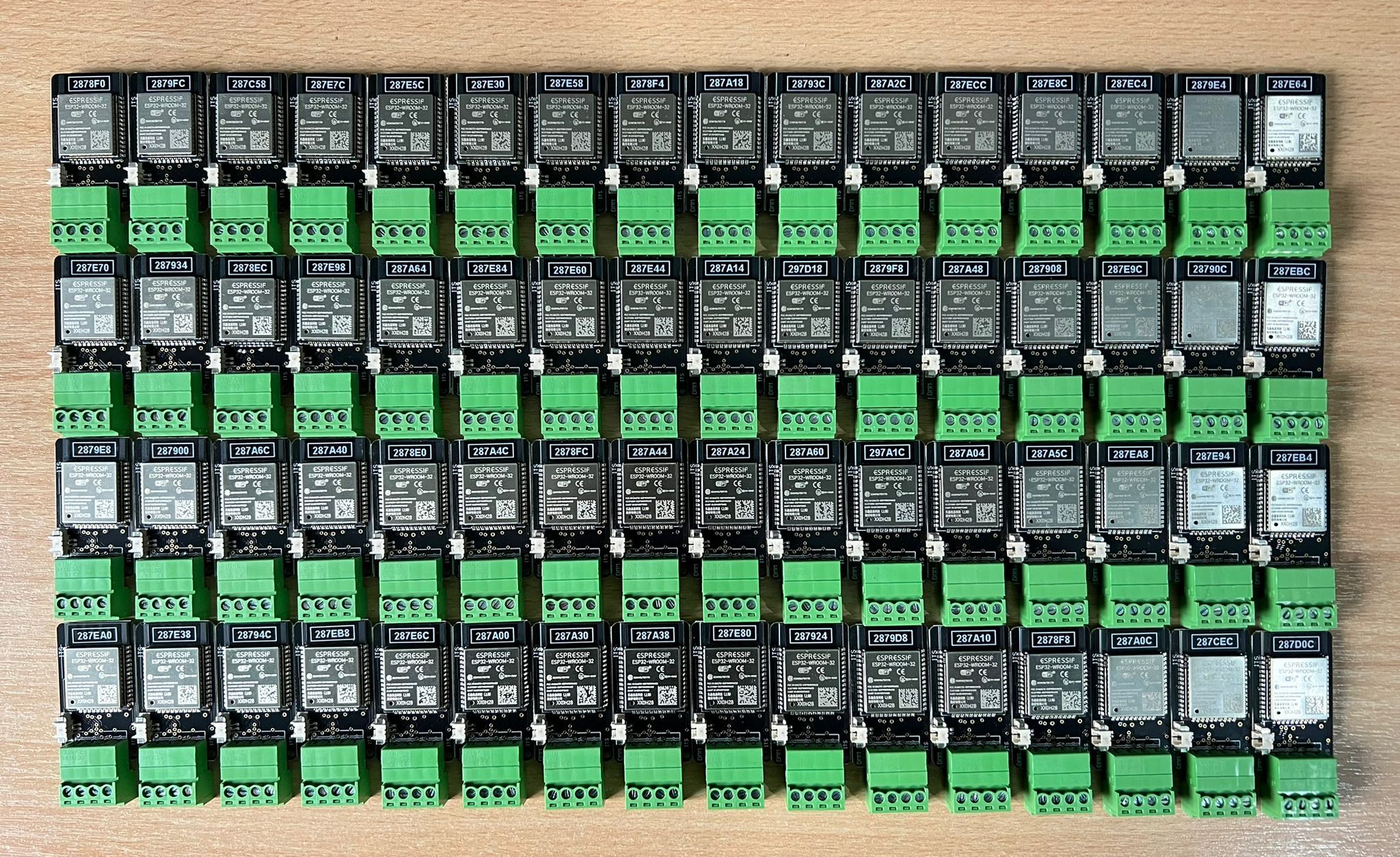
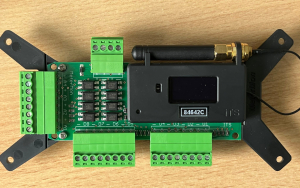
MeterMon (MM8)
The MeterMon component is integral to our Energy Management solution (product name: MMEM).
It’s called MM8 because it has eight inputs, enabling it to monitor up to eight different utilities meters. This could include water, electricity, gas etc. In the case of a very large building, the eight inputs could be split between floors or wings of the building.
MM8 has an OLED display that shows the count for all eight inputs. Operations personnel can see in real-time the count for these inputs.
Prior to installing MM8, operations personnel would have been working with legacy systems without a display. Often, they’d have to check the pulse of the meter to ensure it was working. The advantage of the OLED display is that they can see the meter is working without having to get any tools out of their toolbox.
MeterMon (MM8)
Dark spaces need the Dark MeterMon (DMM)
Many buildings have utilities meters in out-of-the-way places. This could include some scary places — dark basements, manholes, and underground tunnels filled with water.
This is where a robust product like the Dark Meter Mon is needed.
The DMM runs on battery and doesn’t need any plug-in power.
DMM has two inputs, because it cannot hold as much metering since it doesn’t get plugged into the mains electrical supply. The product does not have a display, because that would be a waste of energy, since these meters are not visited by a human very often.
Each DMM is encapsulated inside an IP66 junction box, so that it will not get contaminated with water if the surrounding space were flooded.

DarkMeterMon

DarkMeterMon (DMM) with one blue battery in an IP66 junction box
Working together for one Smart Building solution
In general, one-quarter of the metering devices that we install, are DMM. Three-quarters are MM8 devices which are plugged into the mains.
Both devices give meter readings once every 30 minutes.
Where the data lives
In real-time, our metering devices capture signals from all over the building, and the data is interpreted by our analytics engine. This data is stored and analysed in Amazon Web Services (AWS) – the most secure cloud system that one can have at the present time.
Network strength and the magic of LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN stands for ‘long range, low power.’ It can penetrate deep into buildings, and it means that few gateways are needed to connect all the meters in a building.
The low power requirements mean that a battery can potentially last for 10 years.
There are other unique features of using LoRaWAN. In the public sector, in buildings like hospitals, security is the most important aspect of any solution. Our metering solution provides multiple layers of encryption, supports multiple gateways, cellular networks, and various levels of data backup. This ensures secure and reliable data transmissions, receival and storage.
LoRaWAN is a breakthrough technology that has enabled connections in buildings that never would have been possible. In older public sector buildings – for example, Belfast’s City Hospital – the walls were built to withstand heavy artillery impacts during war period. The walls are impenetrable and extremely thick. It is notoriously difficult for wireless signals to pass through the building uninterrupted. With our technology, we were able to run two wires up and down through the elevator shaft, through all 11 floors of the hospital, and with RS485 connections, the signals can connect all floors. With a master device at the top, and slave devices at each floors, every floor can “talk” to the master devices as MM8s connect their signals via two twisted pair wires and transmit out at the top of the building to the LoRaWAN gateways.
Our CEO summed this up by saying “To boldly go where no device has gone before!”
Summary
With the combination of metering technology that can be installed literally anywhere – and a LoRaWan-based network that connects each meter to the data analytics dashboard – every unit of energy used in the Smart Building is monitored.




